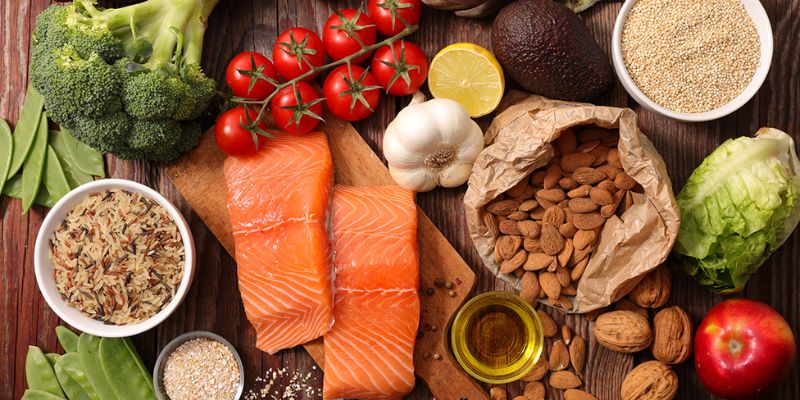
Please ignore the fact that it's called type 2 diabetes; more than 90 percent of individuals who have diabetes have it. And a sizeable minority are unaware that they even have the condition. So, what are the telltale signs that it has? How do you prevent complications? Will eating the right foods help you turn back the clock? We are here to provide you with enlightening responses to all the essential questions you have been asking.
What Are The Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes?

There are two main protagonists in this story. In reaction to food consumption and increased glucose levels in the blood, your pancreas will generate insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps your body absorb and use carbs, which then convert into sugar. Insulin is responsible for this process. Because of this, the following things will occur:
- Your muscles, liver, and fat become insulin resistant, which means they no longer respond to insulin and cannot absorb and utilize glucose. This occurs when you have type 2 diabetes.
- The beta cells in your pancreas grow fatigued and cannot continue producing adequate insulin.
Is There a Link Between Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes?
Because obesity and type 2 diabetes are the most common forms of metabolic disease, our understanding of these conditions is essential. Even though these are two different conditions, they frequently coexist.
Because obesity is a disease and the body defends a higher body weight set point, some people never develop obesity, and some people have obesity for whom lifestyle changes do not always work.
Even though lifestyle is essential for the treatment of both diabetes and obesity, some people never develop obesity. Some people do have obese for whom lifestyle changes do not always work.
What Are The Symptoms and Signs Associated with Type 2 Diabetes?
- Polydipsia is characterized by an extreme thirst much more intense than the sensation you receive when it's hot outside. You may suffer from polydipsia if drinking water does not satisfy your hunger, and the majority of the time, your mouth feels cottony and dry.
- Hyperphagia refers to an unquenchable hunger worse than the hangry feeling you experience when skipping meals since it has no end in sight. You may have hyperphagia if, after eating a complete and well-balanced meal, you keep coming back for more food even if you don't feel satisfied.
- The need to urinate more frequently than usual is called polyuria. Urinating more frequently than seven or eight times a day may indicate a person has type 2 diabetes. The frequency of toilet trips might vary from person to person according to their lifestyle, the drugs they are taking, and the amount of liquid they consume.
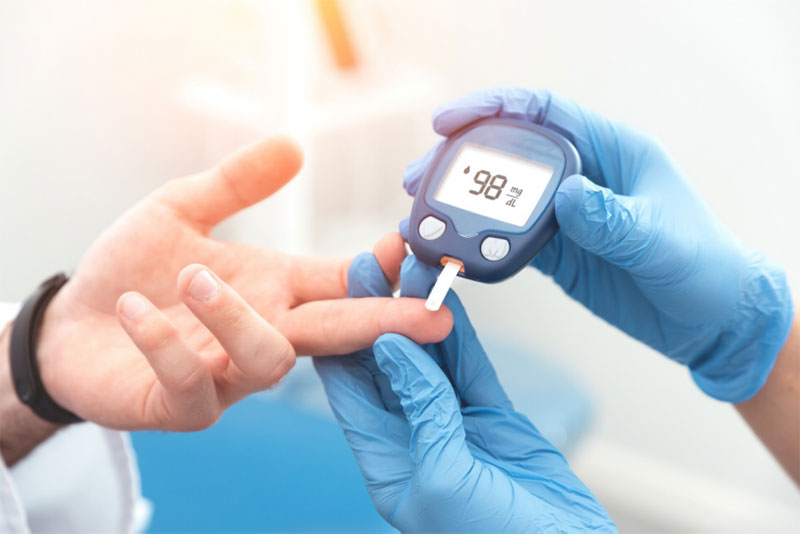
How Do Doctors Usually Identify Type 2 Diabetes?
The diagnosis and ongoing management of type 2 diabetes often involve using the hemoglobin A1C test, which determines your average blood sugar levels. It is a measurement of the glucose bound to hemoglobin, and it shows the average amount of glucose present in the blood over the last two to three months.
The conclusion is expressed as a percentage. If you have been diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, your blood sugar levels are more significant than usual, often indicated by a hemoglobin A1C result of 6.5% or above. Prediabetes might be characterized by an A1C effect that falls between 5.7% and 6.4%.
What Exactly Is Pre-Diabetes?
When your blood sugar levels are high but not high enough to diagnose you with type 2 diabetes, you are said to have prediabetes. The fact that prediabetes is more straightforward to correct than type 2 diabetes is the single most crucial fact about this condition. A diagnosis of prediabetes should be viewed as an opportunity to prevent the progression from typing two diabetes.
Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: What's Different?
There are several vital distinctions to be made between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, including the following:
- Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder. Diabetes type 1 is a condition that can only be controlled and managed; it cannot be cured. Reversal of type 2 diabetes is possible with the use of appropriate treatment and the adoption of healthier lifestyle habits.
- If you have type 1 diabetes, your pancreas cannot make insulin. If, on the other hand, you have type 2 diabetes, your insulin production is limited, and your body's reaction to insulin is diminished, then you have type 2 diabetes.